We all know we should be “increasing our intake of healthy fats” but what does that actually mean? What makes one fat healthy and another fat unhealthy?
Healthy fats are often represented in an unsaturated form, such as those found in oils, nuts, seeds, and fish. These are mostly plant-based and liquid at room temperature. You may see these on labels as polyunsaturated or monounsaturated. Consuming these types of fats acts positively on cholesterol levels, improves triglycerides, contributes to cell membrane health, nerve function and blood clotting, and reduces inflammation.
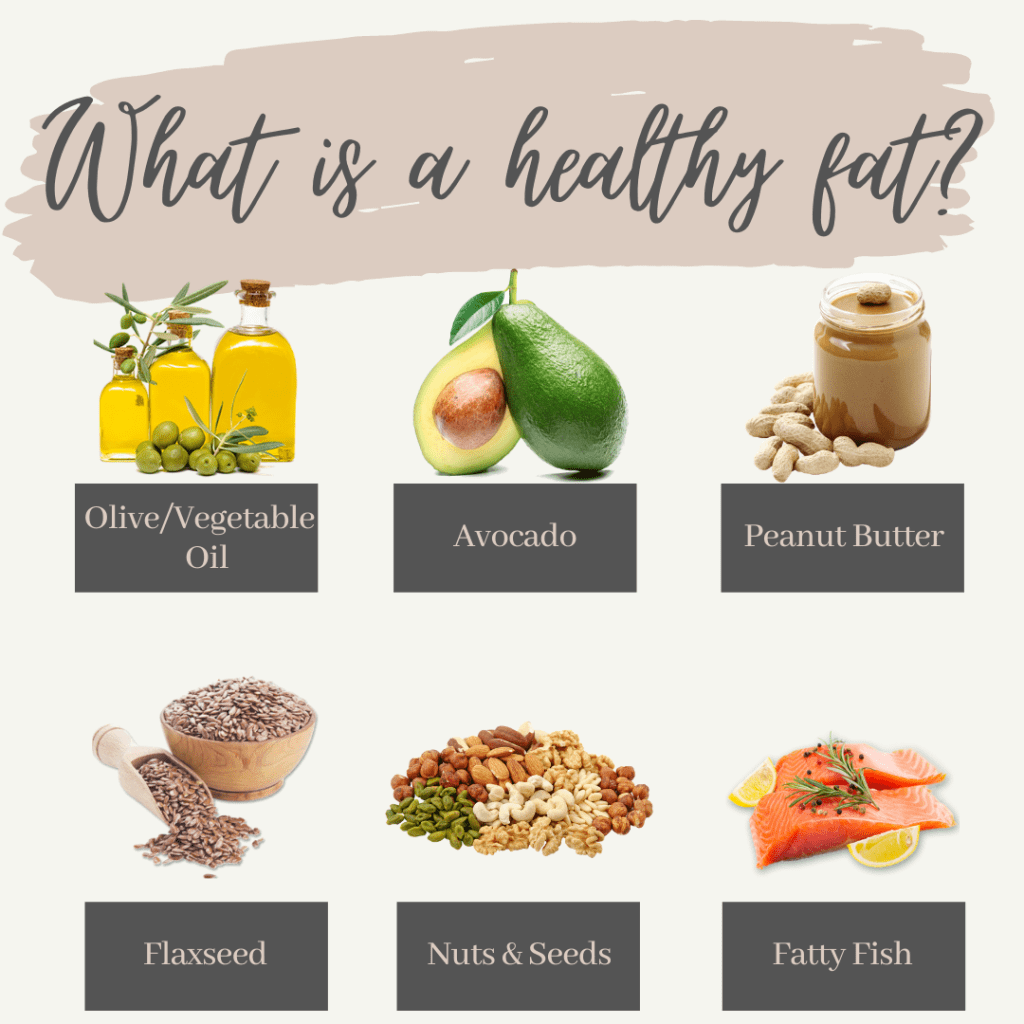
Especially important to our health are Omega-3 fatty acids, like those found in fatty fish, walnuts, flax and soybean. Omega-3 fatty acids play an important part in preventing heart disease, reducing blood pressure, raising HDL (“good cholesterol”) levels, lowering triglycerides, and some studies have hinted reducing the risk of dementia.
Unhealthy fats on the other hand, come mostly in the form of saturated fats. These are easy to identify as they’re almost always from animal sources (butter, dairy, fatty meats, proteins with skin on) but may be from plants, such as coconut. These are solid at room temperature. Saturated fats have a negative impact on heart health, cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Take a look at the icons above to see some popular sources of healthy fats! Yes, even peanut butter! Though peanut butter does have some saturated fat, it is more composed of unsaturated fat and is also a good source of protein.
